Generally, it’s an easy way to reset the root password if you’re already logged in with the root privileges. However, if you forget the password and need to change it, here’s an article for you.
To reset the root password on CentOS7/RHEL 7, you need:
- A working GRUB root loader
- A working operating system
Steps to Reset Root Password on CentOS 7/RHEL 7
Method 1: Rebooting and Editing Grub2
Reboot the system and press any key to auto-boot from the default kernel. Then, press “e” after selecting the kernel line to enter the Grub Edit Mode
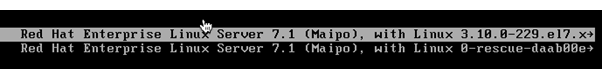
After you press the “e” key, scroll down, go to the Linux 16 line, and remove the rhgb, quiet and LANG parameters.
For moving at the end of the line, press ctrl+e, move to the front, and press ctrl+a.
The Linux16 line will be linuxefi on the UEFI system.
Method 2: Appending the rd.break to kernel
When you are in edit mode, go to the line starting with linux16 and append rd.break at the end of this line.
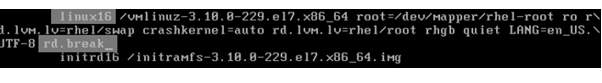
This will make the machine boot into emergency mode, giving you root user privileges without entering a root user password. Even though the root user hasn’t been set, this still works.
Reboot the System
Press CLTR+x after appending the rd.break to the kernel. This will help to reboot the system into emergency mode.
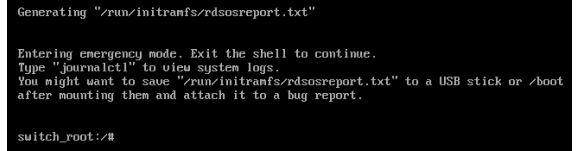
Remounting the sysroot
Firstly, we will remount the sysroot file system in read-write mode and then use the chroot to get into a chroot jail.
# mount -o remount, rw/sysroot
# chroot /sysroot
Resetting the Root Password
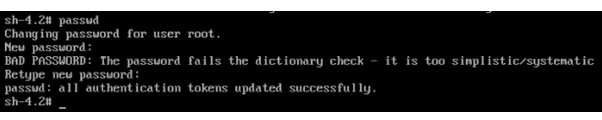
Type a password command in the command line and set the new password for the root user. You might even get into some warnings like “password fails directory check” if your password is weak. You can ignore the warning and set the password you want.
# passwd
SElinux relabeling
All the unlabeled files, which include the shadow files, get relabelled during the booting. The hidden files auto-relabel the files changed outside their regular context, like the file/etc/shadow.
# touch /.autorelabel
Sync
If you want to flush the cache of the disk, type the command given below:
# sync
Reboot
Type the exit command twice and leave the chroot environment and log out. The system will apply some SELinux contexts and reboots.
Conclusion
By following the steps given above, you can easily login to CentOS/RHEL using the new password.